See also Designing Pay Levels, Pay Mix and Pay Structure and Pay Employment Benefits
decision for externally competitive pay levels and structure.
- employer’s competitive pay policy
- purpose of survey
- construct market line.
- balance competitiveness with internal alignment through pay range, flat rates, bands
survey.
- adjust pay level
- pay mix: stock, benefits
- pay structure: job evaluation results.
- estimate competitors’ labour costs (competitive intelligence)
design
Which job to include?
- benchmark job approach, low-high approach, conversion/survey level What information to collect?
- organisation data, total compensation data, information about incumbent
interpretation
Verify anomalies, accuracy of match, validation to other trends.
select relevant market competitors
- Relevant labor markets
- Fuzzy markets: new orgs/orgs with unique jobs fuse diverse factors for relevant markets fuzzy
Question
What factors determine the relevant market for pay surveys? Why is the definition of the relevant market important?
- Industry and Job Function: depending on the job sector and industry size.
- Geographic Location: location-based pay
- Experience and Education Level: pay for experience and education
- Market trends: market trends and changes
importance because:
- Competitiveness: to attract and retain employees.
- Fairness and Equity: enhance satisfaction and reduce turnover.
- Legal compliance: to avoid discrimination.
organization
| Basic Elements | Examples | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Identification | Company name, address, contact person | Further contacts |
| Financial performance | Assets, sales, profits (after taxes), cashflow | Indicates nature of the product/service markets, the ability to pay, size and financials |
| Size | Profit centres, product lines | Importance of specific job groups to business success |
| Total number of employees | Impact on labour market | |
| Structure | Organizational charts | Indicates how business is organized and how important managerial jobs are. |
Total compensation
- cash forms used
- non-cash forms used
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Base pay | Tells how competitors are valuing the work in similar jobs. | Fails to include performance incentives and other forms, so will not give true picture if competitors offer low base but high incentives. |
| Total cash | Tells how competitors are valuing work; also tells the cash pay for performance opportunity in the job. | Not all employees may receive incentives, so it may overstate the competitors’ pay; plus, it does not include long-term incentives. |
| Total compensation (base + bonus + stock options + benefits) | Tells the total value competitors place on this work. | All employees may not receive all the forms. Don’t set base pay equal to competitors’ total compensation. |
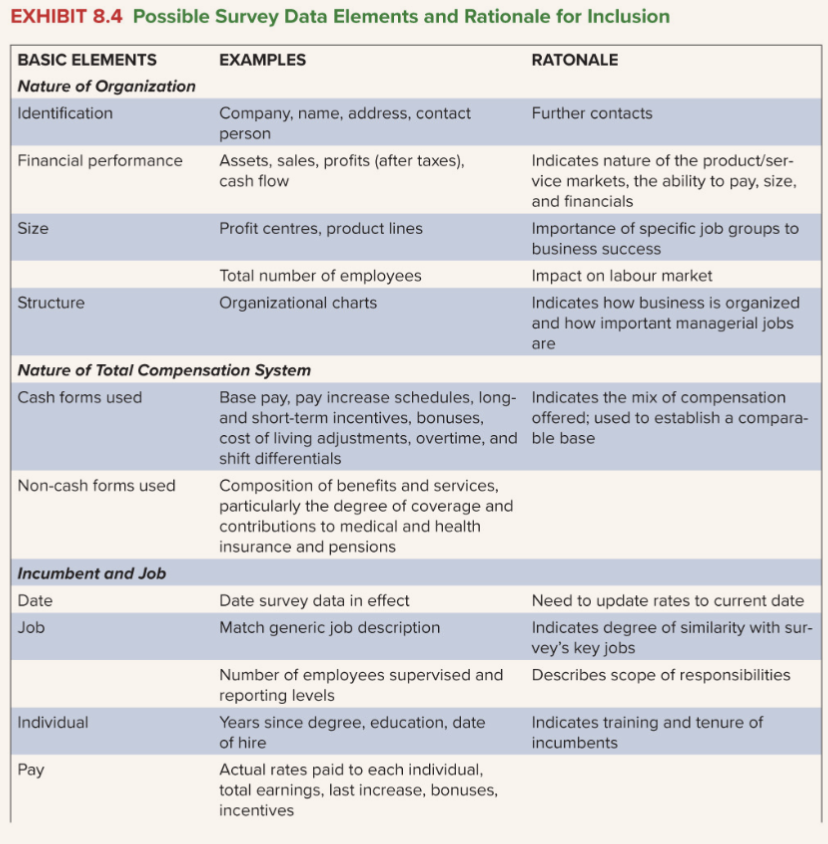
incumbent & jobs
| Basic Elements | Examples | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Date | Date survey data in effect | Need to update rates to current date |
| Job | Match generic job description | Indicates degree of similarity with survey’s key jobs |
| Individual | Number of employees supervised and reporting levels | Describes scope of responsibilities |
| Years since degree, education, date of hire | Indicates training and tenure of incumbents | |
| Pay | Actual rates paid to each individual, total earnings, last increase, bonuses, incentives |
hr outcomes.
| Basic Elements | Examples | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Productivity | Revenues to employee ratio, revenues to labour costs ratio | Reflect organization performance and efficiency |
| Total labour costs | Number of employees x (average wages and benefits) | Major expense |
| Attraction | Yield ratio, number accepting offer to number of job offers ratio | Reveals recruiting success |
| Retention | Turnover rate; number of high or low performers who leave to number of employees ratio | Reveals outflow of people |
| Employee views | Total pay satisfaction | Reveals what employees think about their pay |
market pay line
links a company’s benchmark jobs on horizontal axis with market rates paid by competitors on the vertical axis.
Internal structure and external market rates
- pay-policy line
- pay ranges
pay-policy line
percent above or below market line intend to “lead”, “lag”, or “match” rate.
Develop grades
single grade will have same pay range
pay range
- midpoints where pay-policy line crosses centre of grade, minimum and maximum
- larger ranges in managerial jobs reflect the greater opportunity for performance variants in the work
- firm uses percentiles as maximum and minimums while other establish them separately.
pay disparity among candidates.
- Internal pressures
- recognize performance pay difference with pay
- expectations pay over time
- External pressures
- difference in quality among individuals
- difference in productivity or value variations
- mix of pay forms
range overlap
Overlap ought to be large enough to induce employees to seek promotions.
Broadbanding
collapse salary grades into a few broad bands, each with a minimum and maximum
- flexibility
- career growth
Employee Benefits
- Flexible hours
- WFH: 45% of employees love their jobs (according to Forbes)
- Vacation time and PTO: No timeout more prone to burnt out
- Pay parental leave
part of compensation package, other than pay for time worked.
Growth in Employee Benefits
- Cost effectiveness of Benefits
- Union
- Employer impetus
- Government Impetus
issues.
-
ensure external competitiveness
-
adequacy of benefits
-
Who should be protected?
-
How much choice should employees have among an array of benefits?
-
How should benefits be financed?
Question
How does external equity differ when pay versus benefits?
- Pay is quantifiable regarding monetary values, whereas benefits are objective in terms of equity.