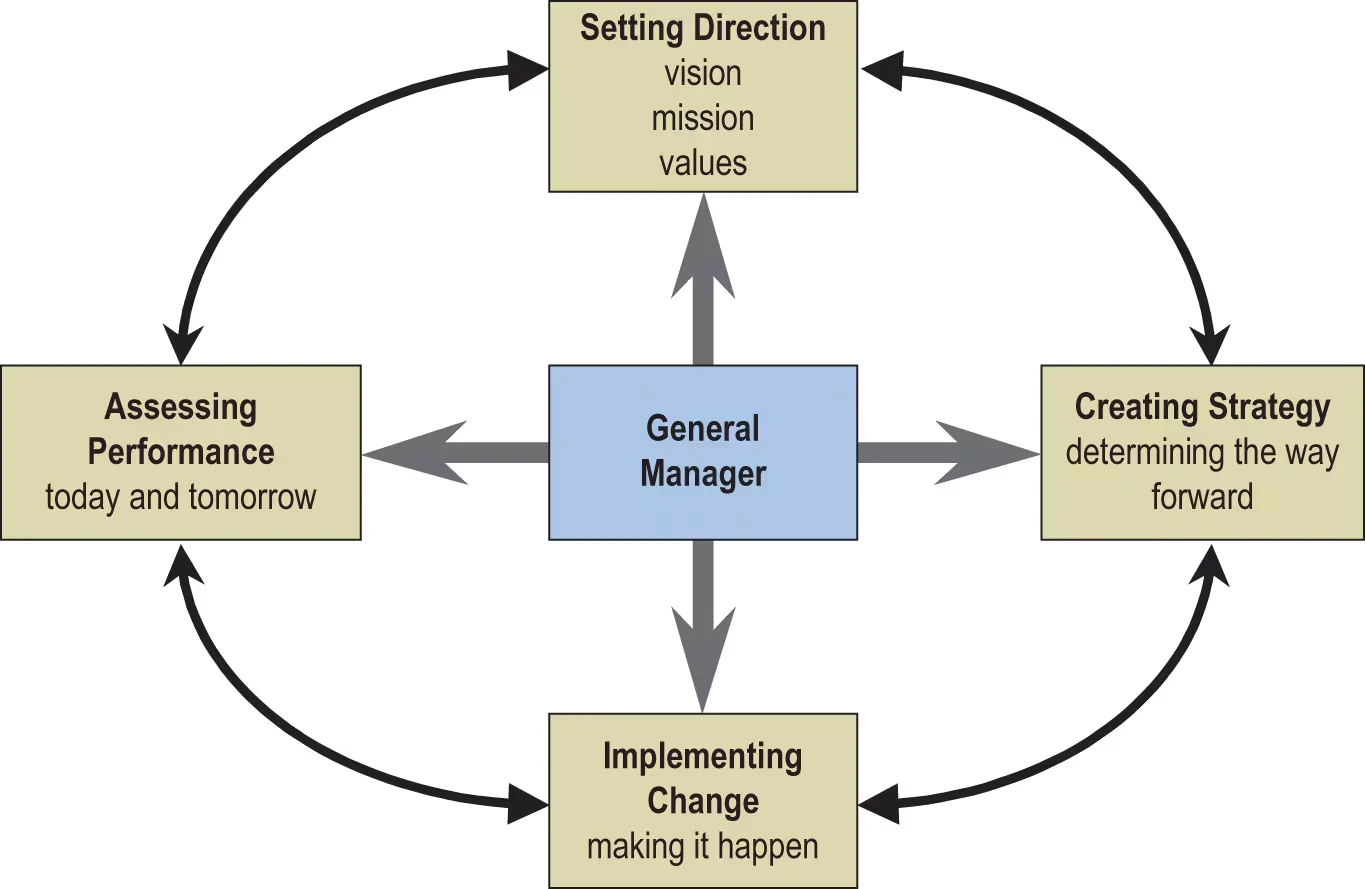
General Manager
- Understanding how strategic issues are viewed from total business perspective
- Applies to general managers, functional managers, and entrepreneurs
- Responsibility for all functional aspects of business
Key Responsibilities
- Setting direction
- Creating strategy
- Implementing change
- Assessing performance
Performance Assessment Areas
- Operating Performance:
- Profitability metrics
- Financial position
- Market performance
- Organizational Health:
- Employee enthusiasm
- Cross-boundary cooperation
- Learning capability
- Sustainability
Critical Challenges
- Managing rapidly changing external environment
- Balancing finite resources
- Adapting strategy to new conditions
- Making trade-off decisions
- Drawing on collective workforce intelligence
Vision & Direction Components
- Guiding Philosophy (core values & purpose)
- Tangible Image (mission & vivid description)
- Measurable objectives
- Implementation plans
Success Factors
- Clear understanding of business purpose
- Ability to make difficult trade-offs
- Balance between short and long-term goals
- Effective communication across organization
- Regular performance monitoring
Strategy
- Concrete expression of how an organization operates in service of its mission
- Applies to all organizations: for-profit, non-profit, small, large, new, mature
- Many organizations have no stated strategy but have implied strategy through actions
1. Goals
- Measurable targets for success
- Two categories:
- Hard goals: quantifiable targets (profit, market share, growth rates)
- Soft goals: social/qualitative targets (employee satisfaction, community impact)
- Must have clear goal structure and priorities
2. Product/Service Market Focus
- Defines what products/services to offer
- Identifies target markets and segments
- Four strategic options:
- Penetration (existing products/existing markets)
- Product development (new products/existing markets)
- Market development (existing products/new markets)
- Diversification (new products/new markets)
3. Value Proposition
- Core benefits offered to marketplace
- Two main types (Porter):
- Low cost strategy
- Differentiation strategy
- Must be:
- Important to customers
- Different from competitors
- Hard for competitors to match
4. Core Activities
- Key activities organization must perform
- Critical to strategy execution
- Must align with other strategy components
- Determines:
- Market control
- Cost structure
- Capabilities
- Flexibility
Strategy Alignment
- All four components must be internally aligned
- Components should reinforce each other
- Misalignment leads to:
- Confusion
- Inefficiency
- Potential failure in competitive markets
What Strategy Is Not
- Not just operational efficiency
- Not just tactical initiatives
- Not just annual budgeting
- Not just strategic priorities without underlying strategy
Corporate vs Business Strategy
see also: pg.30

Business Strategy
- Focuses on single business unit
- Answers: “How should we compete?”
- Deals with competitive advantage within industry
Corporate Strategy
- Manages multiple business units
- Answers: “Which industries should we compete in?”
- Types:
- Pure play (95%+ revenue from one unit)
- Dominant business (70-95% from one unit)
- Related constrained (linked businesses)
- Related linked (limited business connections)
- Unrelated diversification (conglomerate)