See also jupyter notebook and Kaggle
Task 1: SVHN Image Classification Using CNN
class SVHNClassifier(nn.Module, PretrainedMixin):
def __init__(self):
super(SVHNClassifier, self).__init__()
# not specified in spec, but add dropout for stability
self.convblock1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
)
self.convblock2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
)
self.convblock3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
)
# Calculate input size for the first fully connected layer
# Input image: 32x32
# After 3 max pooling layers (32 -> 16 -> 8 -> 4)
# With 128 channels: 128 * 4 * 4 = 2048
self.fc = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128 * 4 * 4, 128), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(128, 10))
def forward(self, x):
x = self.convblock1(x)
x = self.convblock2(x)
x = self.convblock3(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return xNote that we include a small serialisation helpers PretrainedMixin using safetensors:
class PretrainedMixin:
@classmethod
def from_pretrained(cls, filepath, device='cuda'):
model = cls().to(device)
load_model(model, filepath)
model.eval()
return model
def save_pretrained(self, base_path='./model'):
save_pretrained(self, name=self.__class__.__qualname__, base_path=base_path)Plot for training metrics can be found as follow:
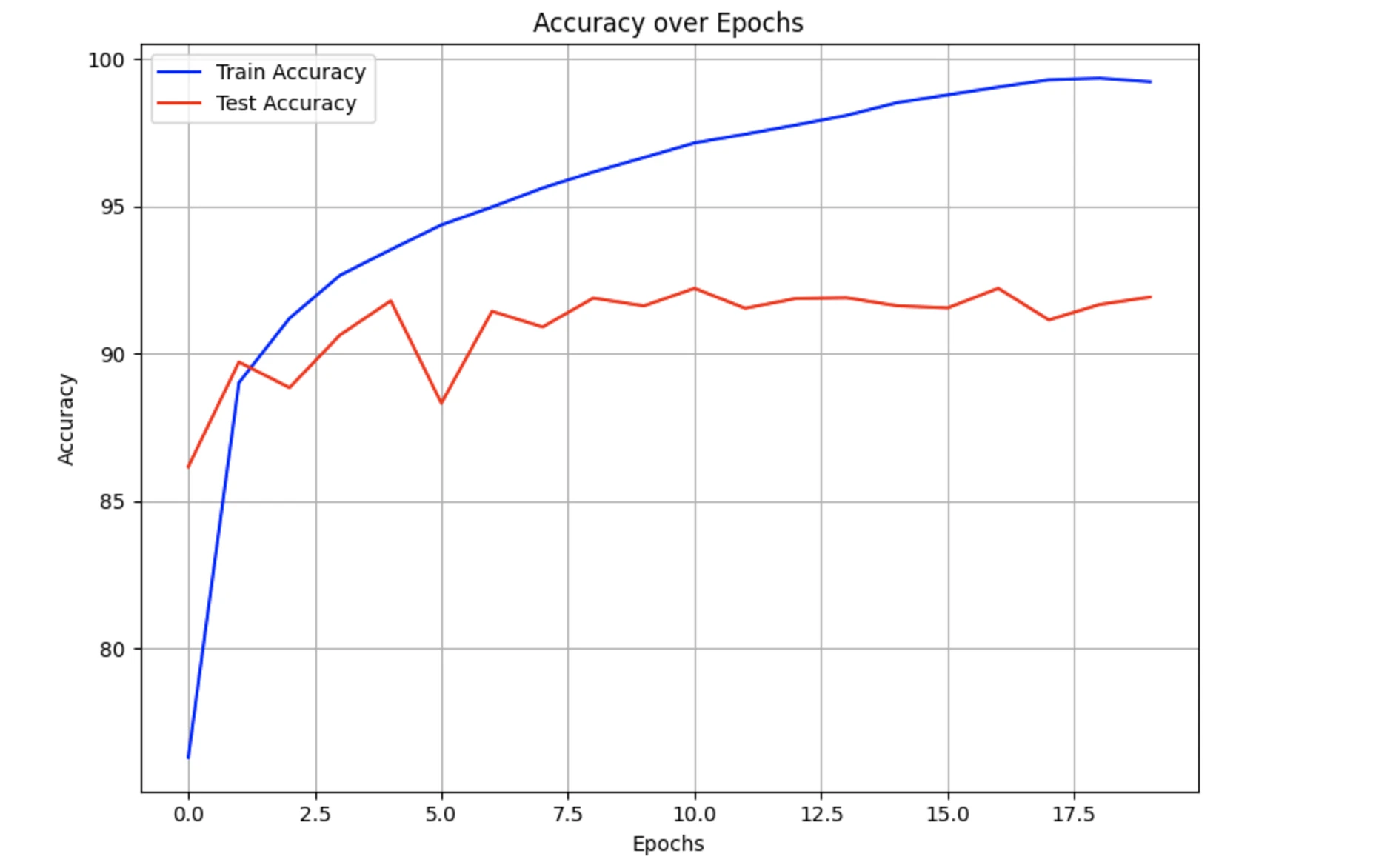
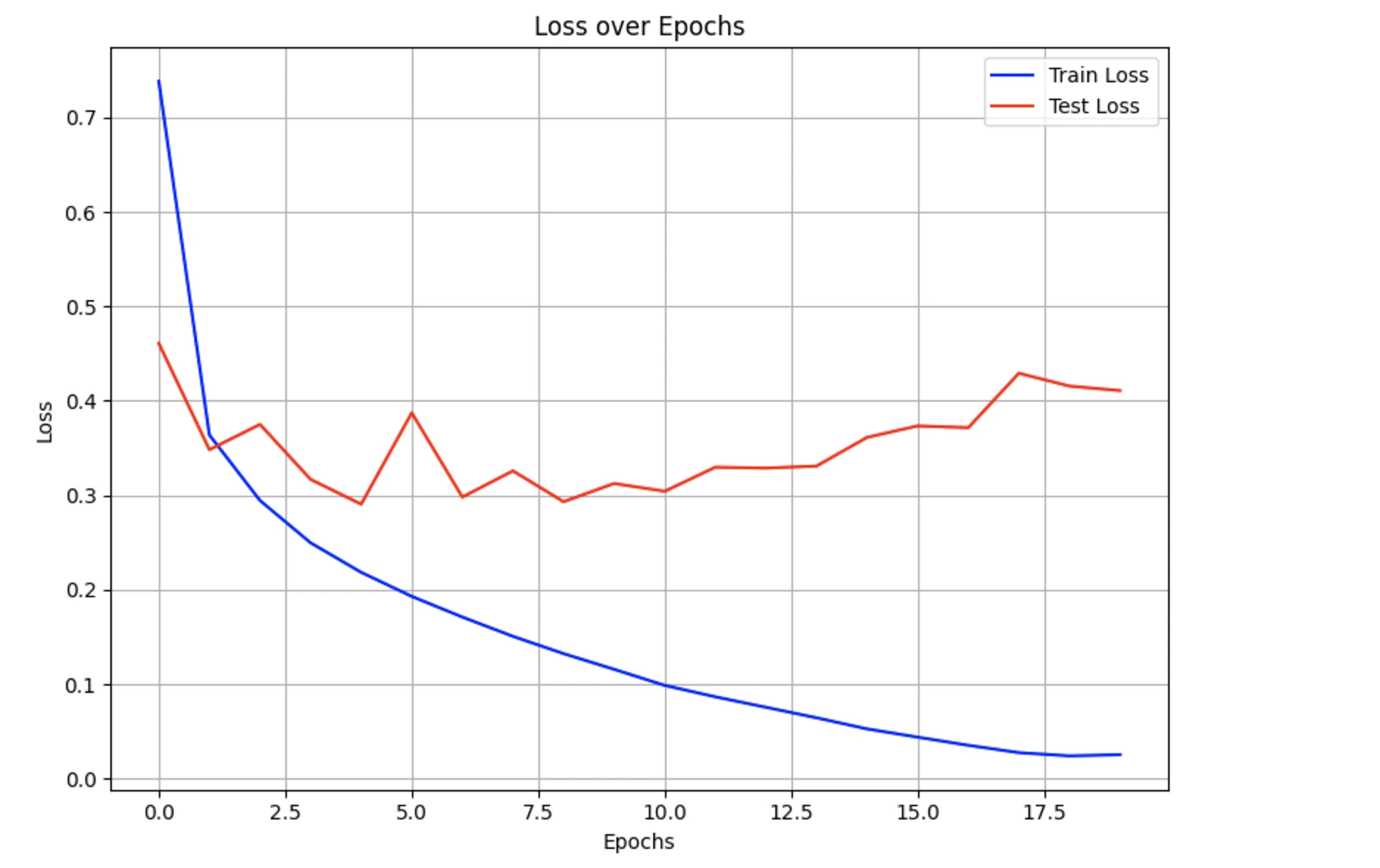
Task 2: CNN for Image Denoising
class ImageDenoisingCNN(nn.Module, PretrainedMixin):
def __init__(self):
super(ImageDenoisingCNN, self).__init__()
# First Convolutional Layer
# Input: 32x32x3 -> Output: 32x32x30
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=30, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
# Second Convolutional Layer
# Input: 32x32x30 -> Output: 32x32x3
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=30, out_channels=3, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
# First conv layer with ReLU
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
# Second conv layer with Sigmoid
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.sigmoid(x)
return xtraining and eval loop:
def train(train_loader, test_loader, model, epochs, loss_function, optimizer, device='cuda'):
"""
Train the model on the training dataset and evaluate it on the test dataset.
"""
# Move model to the specified device
model = model.to(device)
train_loss_epochs = []
test_loss_epochs = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
train_loss_batches = []
# Use context manager for batch progress bar
with tqdm(
enumerate(train_loader), total=len(train_loader), desc=f'epoch {epoch + 1}/{epochs}', ncols=100
) as batch_pbar:
for batch_idx, (clean_images, noisy_images) in batch_pbar:
# Move data to device
clean_images = clean_images.to(device)
noisy_images = noisy_images.to(device)
# Zero the gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Forward pass
denoised_images = model(noisy_images)
loss = loss_function(denoised_images, clean_images)
# Backward pass and optimize
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Track batch loss
train_loss_batches.append(loss.item())
batch_pbar.set_postfix({'batch_loss': loss.item()})
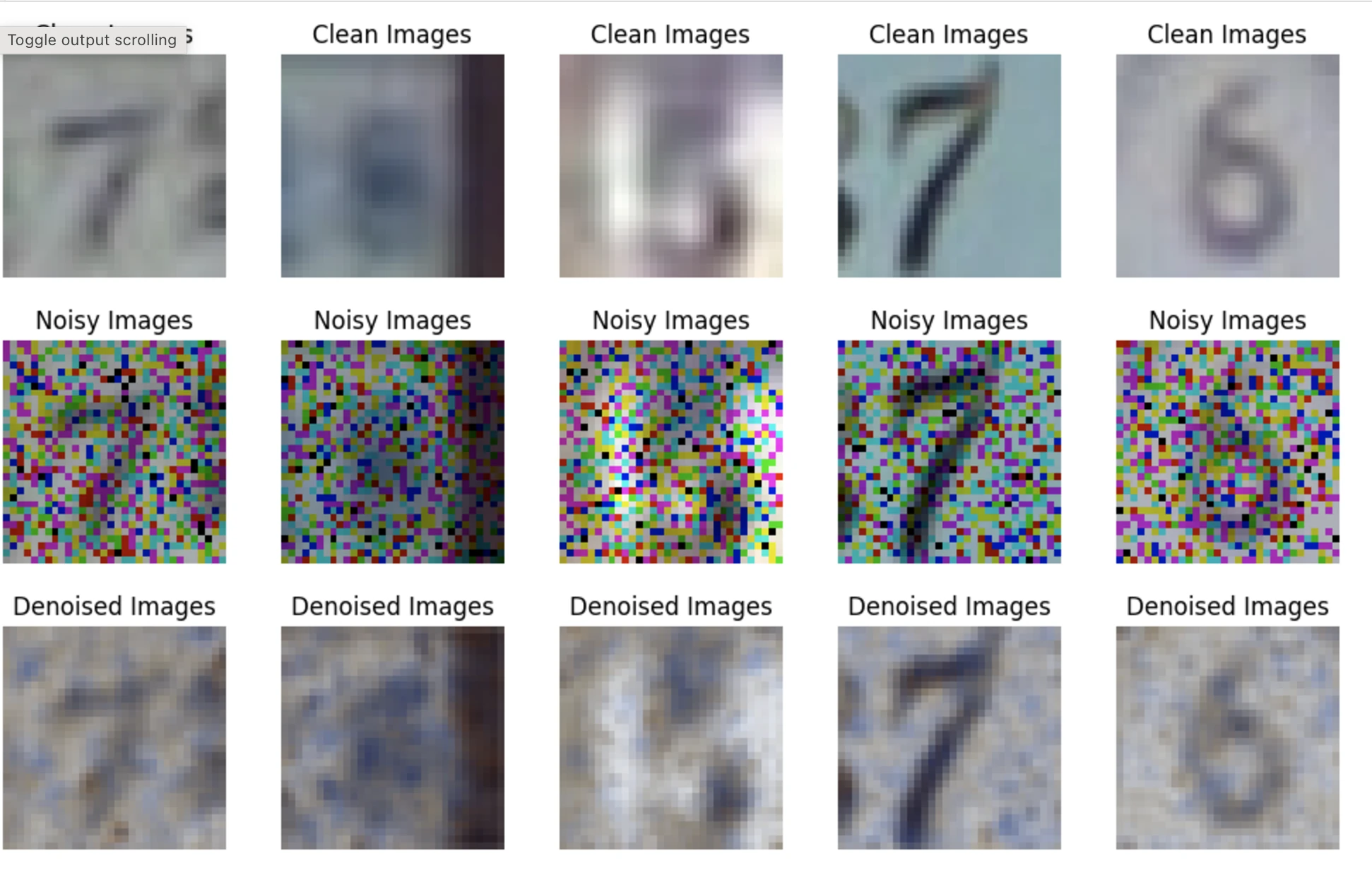
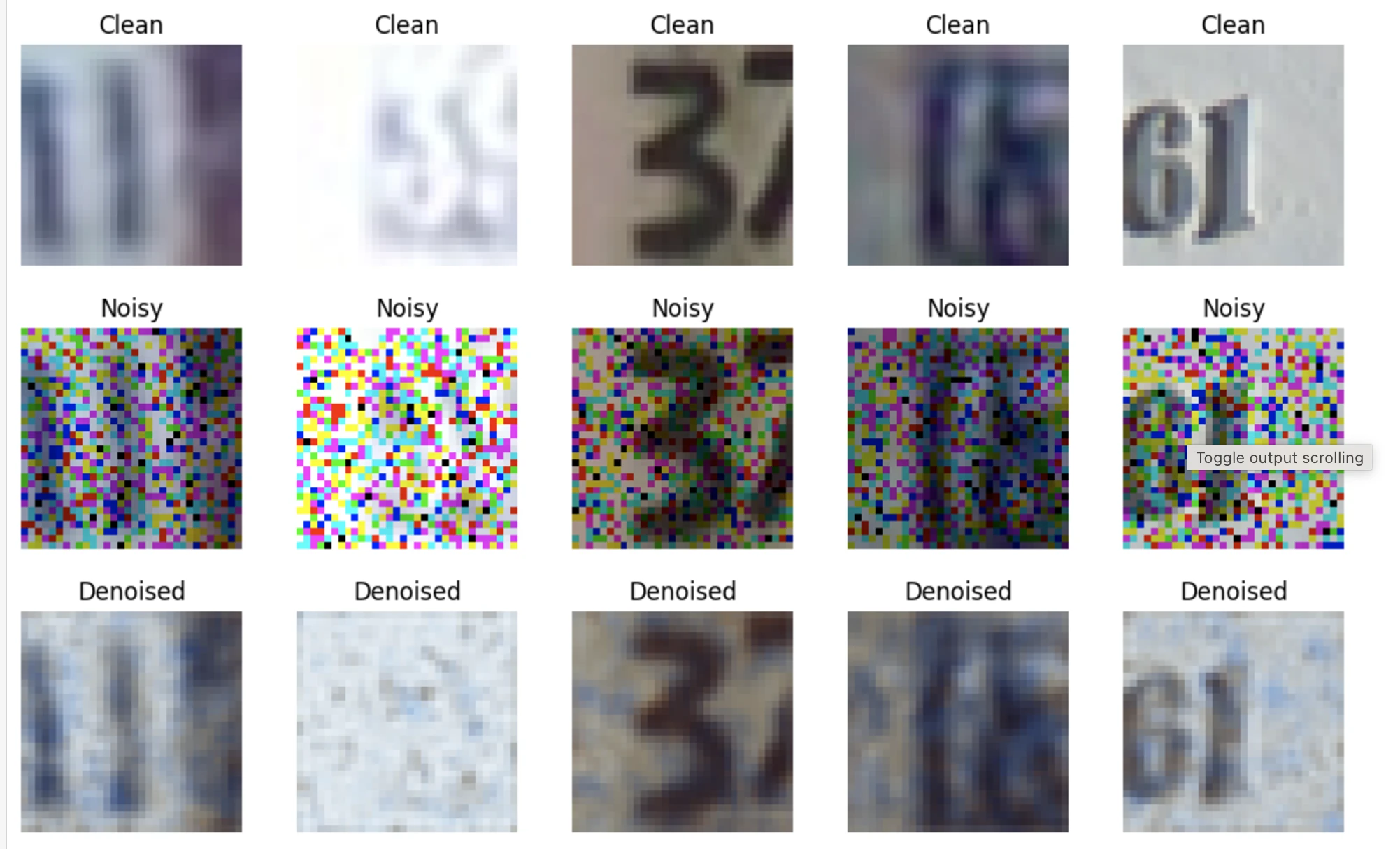
# Display sample results every 5 epochs, at the last batch
if epoch % 5 == 0 and batch_idx == len(train_loader) - 1:
show_images_grid2(clean_images[:5].detach().cpu(), title='Clean', cols=5)
show_images_grid2(noisy_images[:5].detach().cpu(), title='Noisy', cols=5)
show_images_grid2(denoised_images[:5].detach().cpu(), title='Denoised', cols=5)
# Calculate average training loss for the epoch
train_loss_epoch = np.mean(train_loss_batches)
train_loss_epochs.append(train_loss_epoch)
# Evaluate model on test set
test_loss_epoch = evaluate(test_loader, model, loss_function, epoch + 1, num_epochs, device=device)
test_loss_epochs.append(test_loss_epoch)
return train_loss_epochs, test_loss_epochs
def evaluate(dataloader, model, loss_function, epoch, num_epochs, device='cuda'):
"""
Evaluate the model on the test dataset and return the average loss.
"""
model.eval()
test_losses = []
with torch.no_grad():
with tqdm(dataloader, desc=f'eval {epoch}/{num_epochs}', ncols=100) as eval_pbar:
for clean_images, noisy_images in eval_pbar:
# Move data to device
clean_images = clean_images.to(device)
noisy_images = noisy_images.to(device)
# Forward pass
denoised_images = model(noisy_images)
loss = loss_function(denoised_images, clean_images)
# Track batch loss
test_losses.append(loss.item())
return np.mean(test_losses)Last sample for this training loop:

epoch 96/100: 100%|██████████████████████████████| 24/24 [00:00<00:00, 34.90it/s, batch_loss=0.0027]
eval 96/100: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████| 24/24 [00:00<00:00, 80.53it/s]
epoch 97/100: 100%|█████████████████████████████| 24/24 [00:00<00:00, 70.63it/s, batch_loss=0.00307]
eval 97/100: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████| 24/24 [00:00<00:00, 78.39it/s]
epoch 98/100: 100%|█████████████████████████████| 24/24 [00:00<00:00, 69.79it/s, batch_loss=0.00271]
eval 98/100: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████| 24/24 [00:00<00:00, 79.21it/s]
epoch 99/100: 100%|█████████████████████████████| 24/24 [00:00<00:00, 70.38it/s, batch_loss=0.00367]
eval 99/100: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████| 24/24 [00:00<00:00, 79.09it/s]
epoch 100/100: 100%|████████████████████████████| 24/24 [00:00<00:00, 70.95it/s, batch_loss=0.00302]
eval 100/100: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████| 24/24 [00:00<00:00, 78.81it/s]visualisation
# Create the plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Plot training and test losses
epochs = range(1, len(train_loss_epochs) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, train_loss_epochs, label='Training Loss', color='blue', linestyle='-')
plt.plot(epochs, test_loss_epochs, label='Test Loss', color='red', linestyle='-')
# Customize the plot
plt.title('Training and Test Losses Over Time', fontsize=14, pad=15)
plt.xlabel('Epochs', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('Loss (MSE)', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.7)
plt.legend(fontsize=10)
# Add minor gridlines
plt.minorticks_on()
plt.grid(True, which='minor', linestyle=':', alpha=0.4)
# Adjust layout and display
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Print final losses
print(f'Final Training Loss: {train_loss_epochs[-1]:.6f}')
print(f'Final Test Loss: {test_loss_epochs[-1]:.6f}')yields the following:
Final Training Loss: 0.003326
Final Test Loss: 0.003811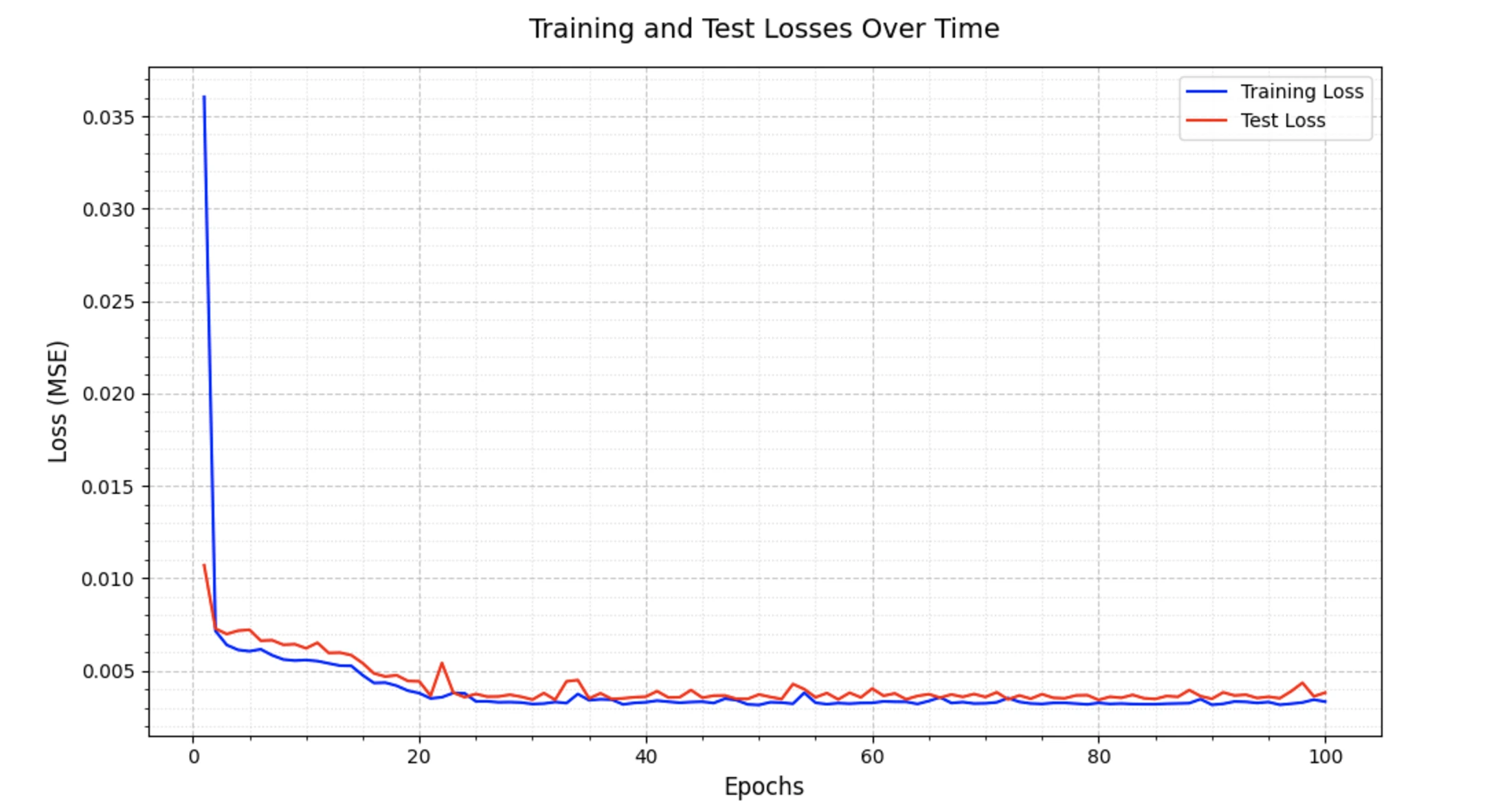
denoising last five samples
Average Test Loss on classes 5-9: 0.003754